Lock
Nov 3, 2023
# Deadlock
- Dijkstra’s Banker’s Algorithm
- What causes deadlock?
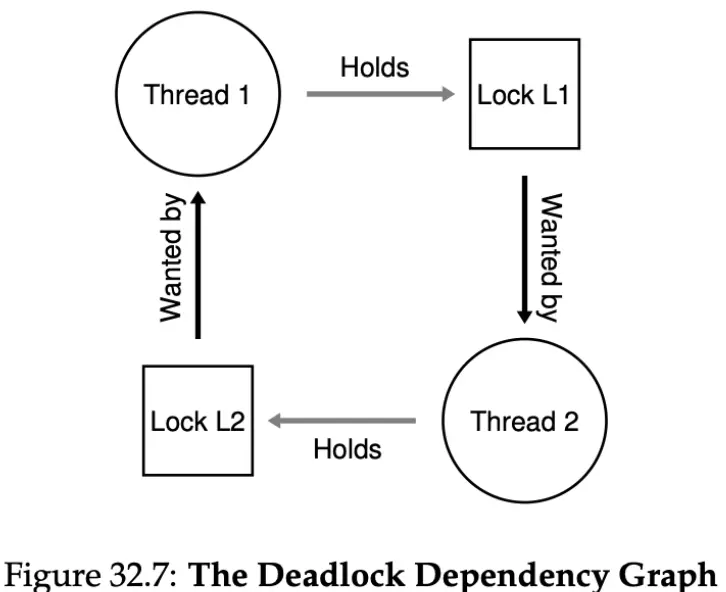
- Mutual exclusion: Threads claim exclusive control of resources that they require (e.g., a thread grabs a lock).
- Hold-and-wait: Threads hold resources allocated to them (e.g., locks that they have already acquired) while waiting for additional resources (e.g., locks that they wish to acquire).
- No preemption: Resources (e.g., locks) cannot be forcibly removed from threads that are holding them.
- Circular wait: There exists a circular chain of threads such that each thread holds one or more resources (e.g., locks) that are being requested by the next thread in the chain.
- How to avoid deadlocks
- Circular Wait
- Hold and Wait
- What to do when deadlock happens
- Kill the one used the least resources.
- Fight for resources (wait for resources).
# Mutex Lock
- A binary Semaphore
It acts as a gatekeeper to a section of code, allowing only one thread to enter at a time and blocking access to all others.
