Log Structured Merge Tree
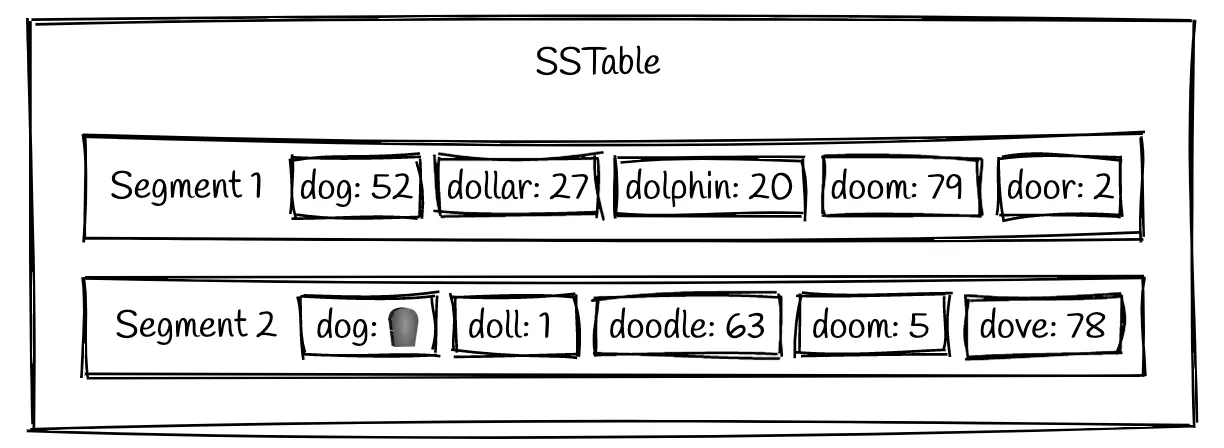
LSM trees are persisted to disk using a Sorted Strings Table (SSTable) format. It is a format for storing key-value pairs in which the keys are in sorted order.
The main reason why LSM provides high write throughput is that every write request is actually performed only “in-memory” in contrast to traditional B-Tree based implementation where the updates are done to disk which can trigger an update to an index making it very expensive.
# Writing Data
An SSTable will consist of multiple sorted files called segments. These segments are immutable once they are written to disk.
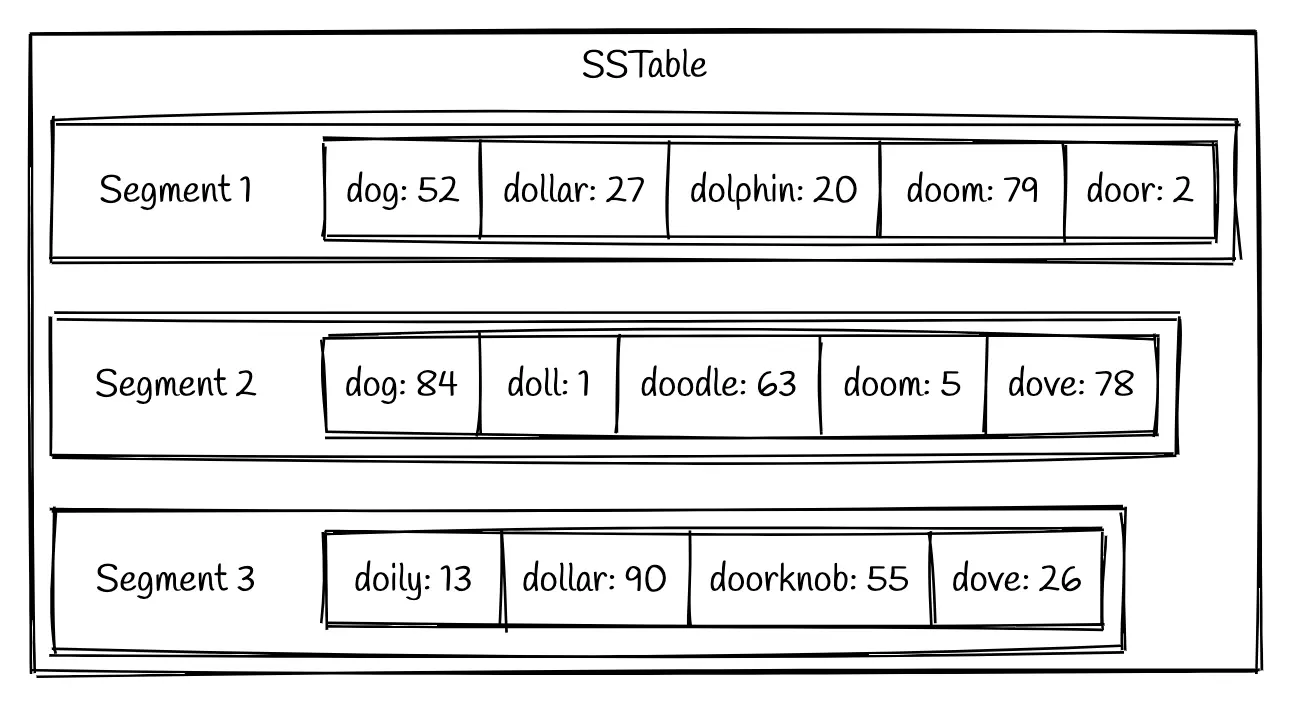
The data writes get stored in a Red Black Tree until the tree reaches a predefined size (memtable). Once the Red Black Tree has enough entries, it is flushed to disk as a segment on disk in sorted order. This allows us to write the segment file as a single sequential write even though the inserts may occur in any order.
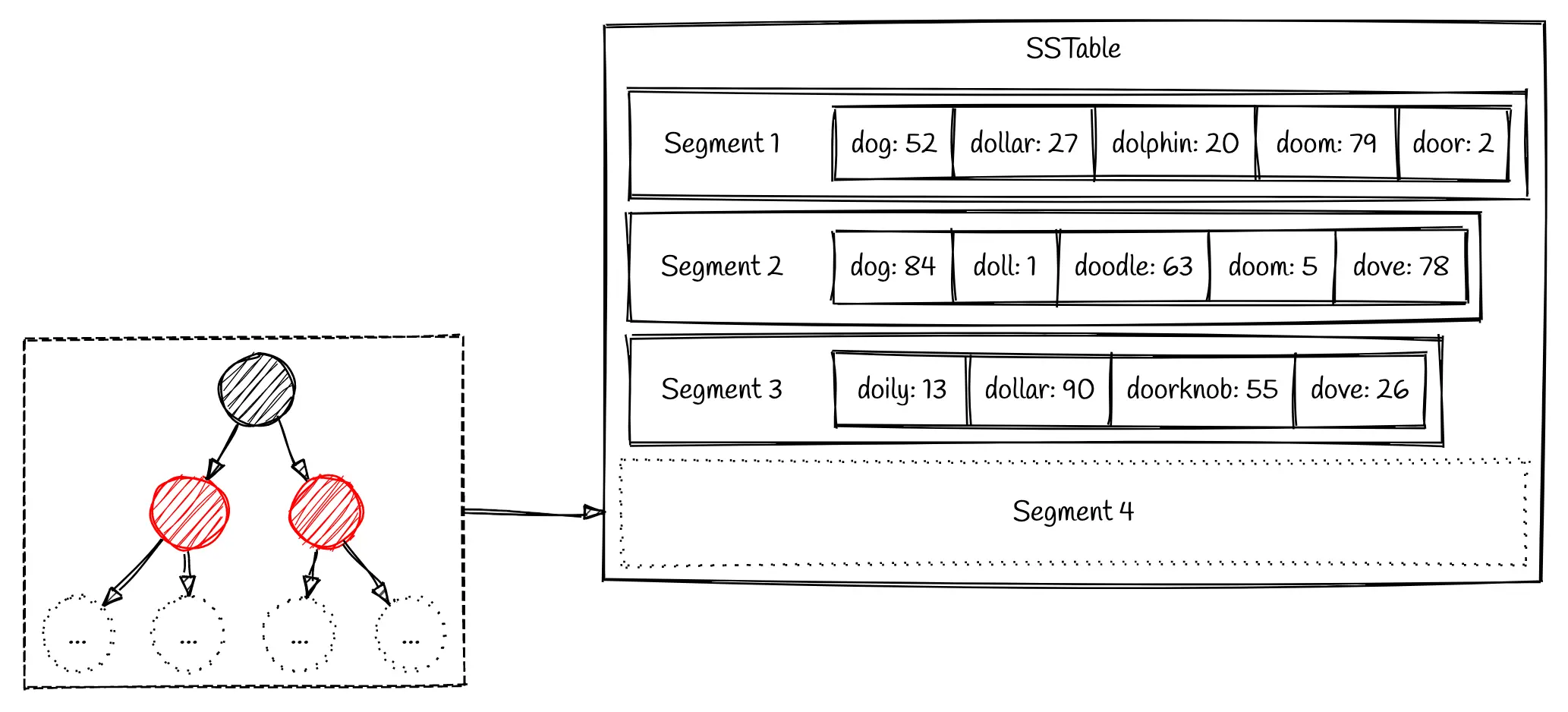
# Reading Data
First check the in memory data structure, then search the sorted tables on disk.
We can use sparse index and Bloom Filter to optimize read performance on disk.
# Sparse Index
A sparse index is an index that does not include all documents in a collection, but only a subset of them. This can be useful when there are many documents in a collection, but only a small subset of them are frequently accessed or queried
But what if the key is not present, in this case we can use a Bloom Filter to tell if a value is missing from our data.
# Compacting Data
Compaction is the process of merging multiple sorted tables into a new, larger sorted table. Once the compaction process has written a new segment for the input segments, the old segment files are deleted.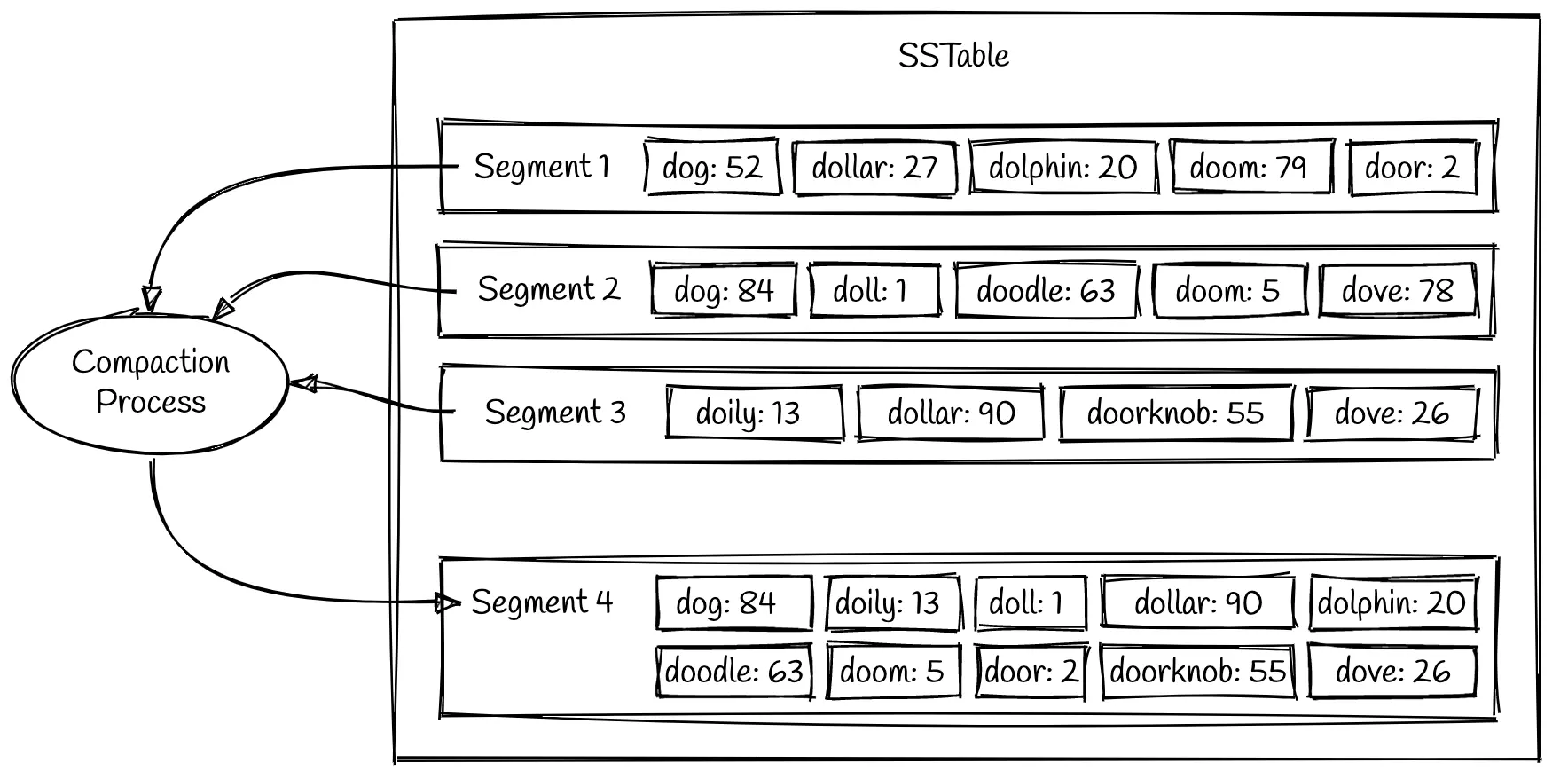
# Deleting Data
In an LSM tree, data is not deleted in place from the log, as doing so would require random I/Os and add overhead to the system.
Deletes actually follow the exact same path as writing data. Whenever a delete request is received, a unique marker called a tombstone is written for that key. Eventually, tombstones will get compacted away so that the value no longer exists on disk.